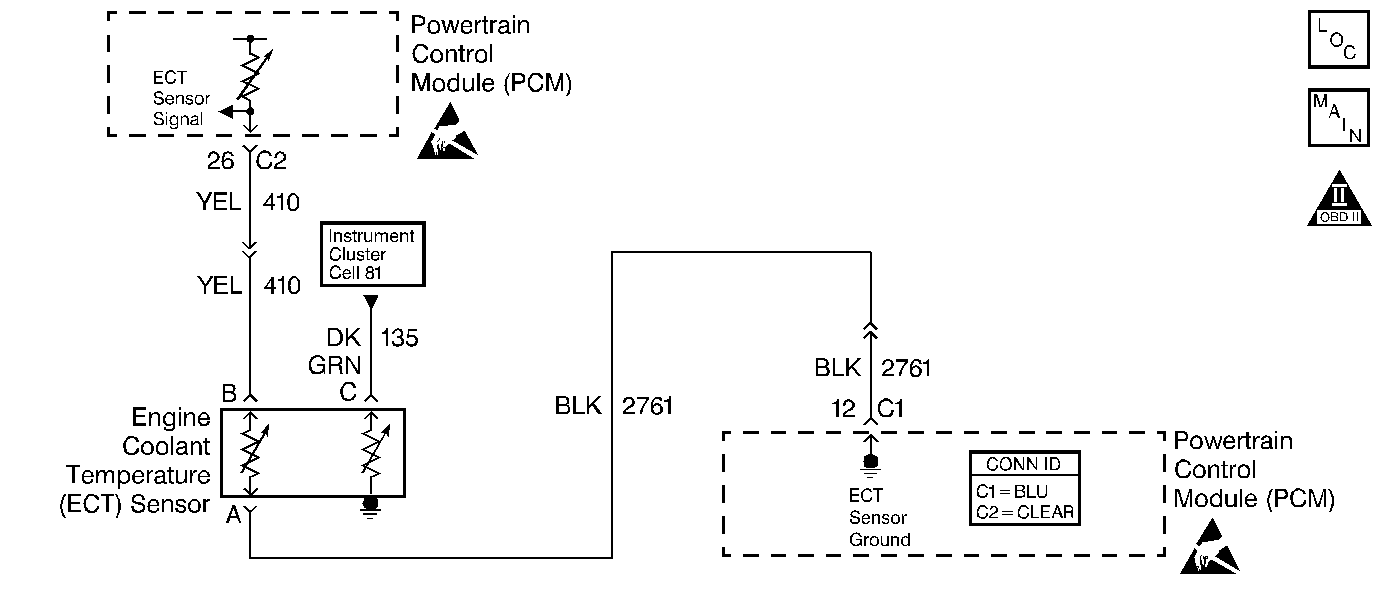
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a thermistor that is mounted in the engine coolant stream. The powertrain control module (PCM) applies approximately 5.0 volts through a pull-up resistor to the ECT signal circuit. When the engine coolant is cold, the sensor, or thermistor, resistance is high and the PCM will measure a high signal voltage. As the engine coolant warms, the sensor resistance lessens, and the ECT signal voltage measured at the PCM drops. With a fully warmed-up engine, the ECT signal voltage should measure from 1.5 volts to 2.0 volts. If the PCM detects an ECT signal volage that is intermittently greater than the range of the ECT sensor, DTC P1115 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine has been running for more than 15 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECT sensor intermittently indicates a coolant temperature that is less than -34°C (-30°F).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM stores conditions which were present when the DTC set as Failure Records only. This information will not be stored as Freeze Frame Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The DTC becomes history when the conditions for setting the DTC are no longer present. |
| • | The history DTC clears after 40 malfunction free warm-up cycles. |
| • | The PCM receives a clear code command from the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect for the following conditions.
Many situations may lead to an intermittent condition. Perform each inspection or test as directed.
Important: : Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Loose terminal connection |
| - | Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| - | Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connection. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness inspection does not reveal a problem, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the scan tool display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Inspect the powertrain control module (PCM) and the engine grounds for clean and secure connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
If the condition is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Snapshot or Freeze Frame/Failure Records may be useful in determining when the DTC or condition was identified.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 | Is DTC P0118 set? | -- | Go to DTC P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit High Voltage | |
3 | Is DTC P1106, P1111, and/or P1121 also set? | -- | ||
4 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
6 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
7 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
8 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
9 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
10 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | System OK |
