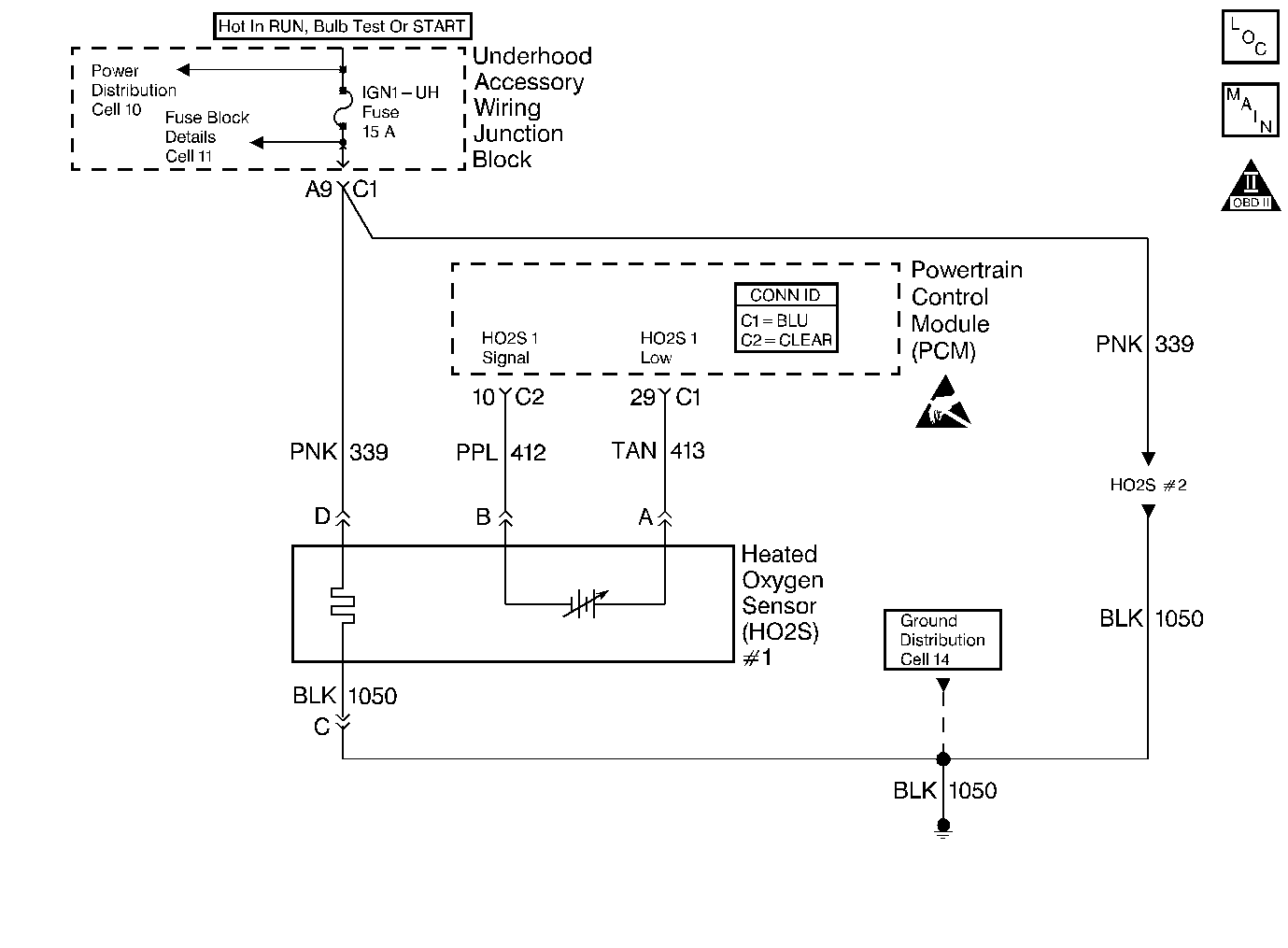
Circuit Description
The PCM supplies a bias voltage of approximately 450 mV between the HO2S signal and the low circuits. When measured with a 10 megaohm DMM, this voltage may display as low as 320 mV. The oxygen sensor varies the voltage from approximately 1000 mV when the exhaust is rich, to 100 mV when the exhaust is lean. During closed loop operations, the PCM constantly monitors the HO2S signal and compensates for a rich or lean condition by decreasing or the increasing injector pulse width. If the HO2S 1 voltage remains excessively high for an extended period of time, DTC P0132 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | None of the following DTCs are active: |
| - | The TP sensor |
| - | The EVAP system sensor |
| - | The misfire sensor |
| - | The IAT sensor |
| - | The MAP sensor |
| - | The fuel trim sensor |
| - | The fuel injector circuit sensor |
| - | The EGR pintle position sensor |
| - | The ECT sensor |
| - | The CKP sensor |
| - | The MAF sensor |
| • | The system voltage is more than 9 volts. |
| • | The closed loop commanded air-to-fuel ratio is between 14:5 and 14:8. |
| • | The throttle angle is between 3 percent and 40 percent. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | During normal closed loop operation, the HO2S 1 signal voltage remains above 975 mV for more than 45 seconds. |
| OR |
| • | During deceleration fuel mode, the HO2S 1 signal voltage remains above 200 mV for more than 55 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check the following items:
| • | The fuel pressure -- The system will go rich if pressure is too high. The PCM can compensate for some increase. If the fuel pressure is too high, a DTC P0132 may be set. Refer to Fuel System Pressure Test (VIN K) or Fuel System Pressure Test (VIN 1) . |
| • | The EVAP canister -- Check the EVAP canister for fuel saturation. If the EVAP canister is full of fuel, check the canister control and hoses. Refer to Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis . |
| • | The mass air flow (MAF) sensor -- Disconnect the MAF sensor and determine whether the rich condition is corrected. If the rich condition is corrected, replace the MAF sensor. Refer to Mass Airflow Sensor Replacement . |
| • | The fuel pressure regulator -- Check for a leaking fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by checking vacuum line to regulator for the presence of fuel. If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator. Refer to Fuel Pressure Regulator Replacement . |
| • | The TP sensor -- An intermittent TP sensor output will cause the system to go rich due to a false indication of the engine accelerating. The Throttle Angle displayed on a scan tool should increase steadily from 0 percent to 100 percent when the throttle opens. If the scan tool display does not increase, check the TP sensor for loose mounting screws. If the TP mounting screws are OK, replace the TP sensor. Refer to Throttle Position Sensor Replacement . |
| • | A shorted heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) -- If the HO2S is internally shorted, the HO2S voltage that the scan tool displays will be more than 1 volt. Disconnect the affected HO2S, and jumper the HO2S low circuit to ground with the ignition ON, and with the engine OFF. If the displayed HO2S voltage changes from more than 1000 mV to approximately 450 mV, replace the HO2S. Silicon contamination of the HO2S can also cause a high indicated HO2S voltage. A powdery white deposit on the portion of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream is an indication of this condition. If you notice contamination, replace the affected HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . |
| • | An open HO2S signal, a low circuit, or a malfunctioning HO2S -- A faulty connection or an open in the HO2S signal or in the low circuit can set a DTC during deceleration fuel mode. An HO2S which is malfunctioning and does not allow a full voltage swing between the rich and lean thresholds can also cause this condition. Operate the vehicle while you monitor the HO2S voltage with a scan tool. If the HO2S voltage is limited to a range of 300 mV to 600 mV, check the HO2S signal, the low circuit wiring, and the associated terminal connections. |
| • | If the wiring and connections are OK, replace the affected HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . |
If you cannot duplicate the DTC and you determine that the DTC is intermittent, review the Failure Records in order to determine when the DTC last set. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
If the vehicle speed is more than 20 MPH and the TP angle is less than 3 percent and this DTC fails during deceleration fuel mode operation, refer to Diagnostic Aids. If this DTC test passes while you duplicate the Failure Records conditions, an intermittent condition is indicated. Review the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed. This may help to determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to set occurs.
-
When the PCM is replaced, you must program the new PCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 |
Important: During this step, observe all H02S voltage parameters. If all parameters remain below the specified value, refer to Diagnostic Aids.
Does the HO2S voltage remain above the specified value? | 600 mV | ||
Operate vehicle in Decel fuel mode, with the vehicle speed above 25 mph, and with the TP angle below 3 percent, while you observe the HO2S voltage parameter on the scan tool. Does the HO2S voltage remain above the specified value while in Decel fuel mode? | 110 mV | |||
4 | Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records conditions. Does the scan tool indicate that this DTC failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
5 | Disconnect the HO2S. Is the HO2S voltage more than the specified value? | 500 mV | ||
6 | Test for a short to voltage on the HO2S signal circuit. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
|
Important: You must program the replacement PCM. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | ||
8 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | System OK |
