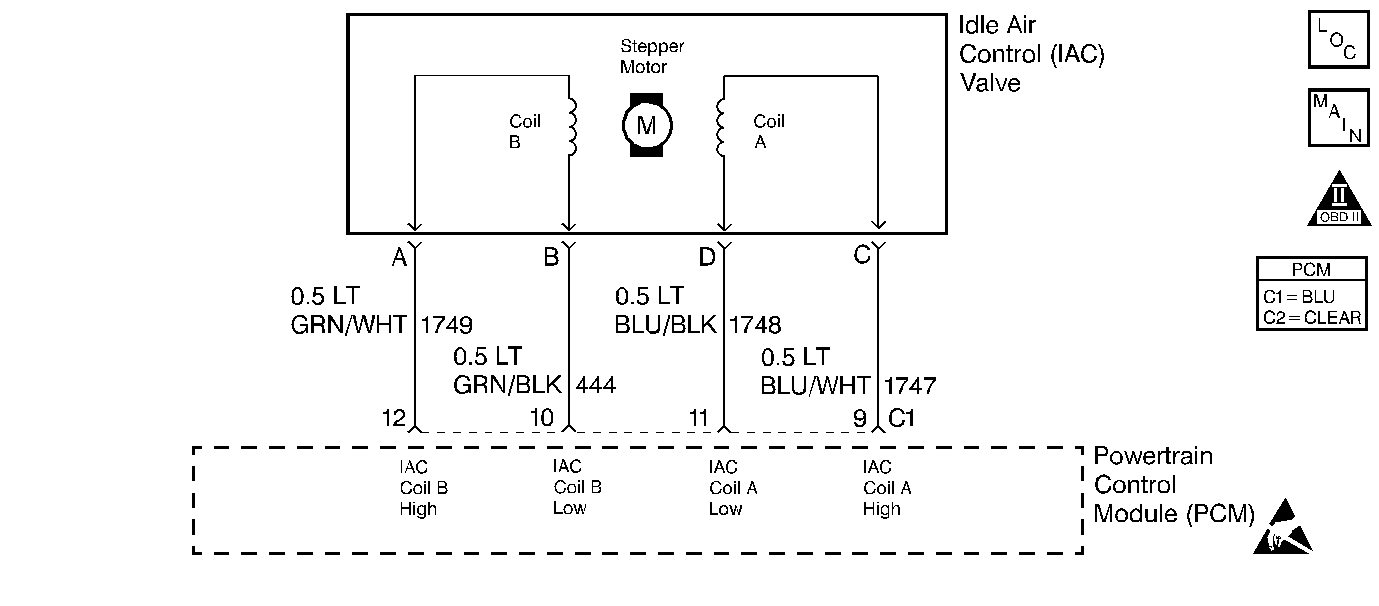
Circuit Description
The PCM controls engine idle speed by adjusting the position of the Idle Air Control (IAC) motor pintle. The IAC is a bi-directional motor driven by two coils. The PCM applies current to the IAC coils in steps (counts) to extend the IAC pintle into a passage in the throttle body to decrease air flow. The PCM reverses the current to retract the pintle, increasing air flow. This method allows highly accurate control of idle speed and quick response to changes in engine load. If the PCM detects a condition where too low of an idle speed is present and the PCM is unable to adjust idle speed by increasing the IAC counts, DTC P0506 will set indicating a problem with the idle control system.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | No active EVAP, misfire, EGR, TP sensor, VSS, ECT sensor, MAP sensor, IAT sensor, Fuel Trim, injector circuit, CKP sensor, MAF sensor DTC(s) active. |
| • | Engine Coolant Temperature is above 70°C (122°F). |
| • | The engine has been running for at least 2 minutes. |
| • | System voltage is between 9-16 volts. |
| • | Vehicle Speed is less than 3 MPH. |
| • | Intake Air Temperature is above -18°C (0°F). |
| • | The throttle is closed |
| • | Engine Speed is more than 175 RPM lower than Desired Idle. |
| • | BARO above 65 kPa. |
| • | Engine run time is greater than 2 minutes. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has been run and passed. |
| • | The History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at PCM or IAC motor. Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. |
| • | Restricted air intake system. Check for a possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted air filter element, or foreign objects blocking the air intake system. |
| • | Throttle body. Check for objects blocking the IAC passage or throttle bore, excessive deposits in the IAC passage and on the IAC pintle, and excessive deposits in the throttle bore and on the throttle plate. |
| • | Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that causes a large vacuum leak, such as a incorrectly installed or faulty CRANKCASE VENTILATION valve or brake booster hose disconnected. |
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is being replaced, the new PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Powertrain OBD System Check | |||||||||
2 | Are any other DTC(s) set? | -- | Go to other DTC first | |||||||||
3 |
Does Engine Speed remain within the specified value of Desired Idle for each RPM command? | ±50 RPM | No trouble found. Go to Diagnostic Aids. | |||||||||
4 |
Does each node light cycle red and green (never OFF)? | -- | ||||||||||
5 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||||
6 | Visually/physically inspect for the following conditions:
Does any of the above require a repair? | -- | Refer to appropriate section for on-vehicle service | |||||||||
7 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||||
8 | Replace IAC valve. Is action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
9 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||||
Replace the PCM. Important: Replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming Is action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||
11 |
Does Engine Speed remain within the specified value of Desired Idle for each RPM command? | ±50 RPM | Repair complete |
