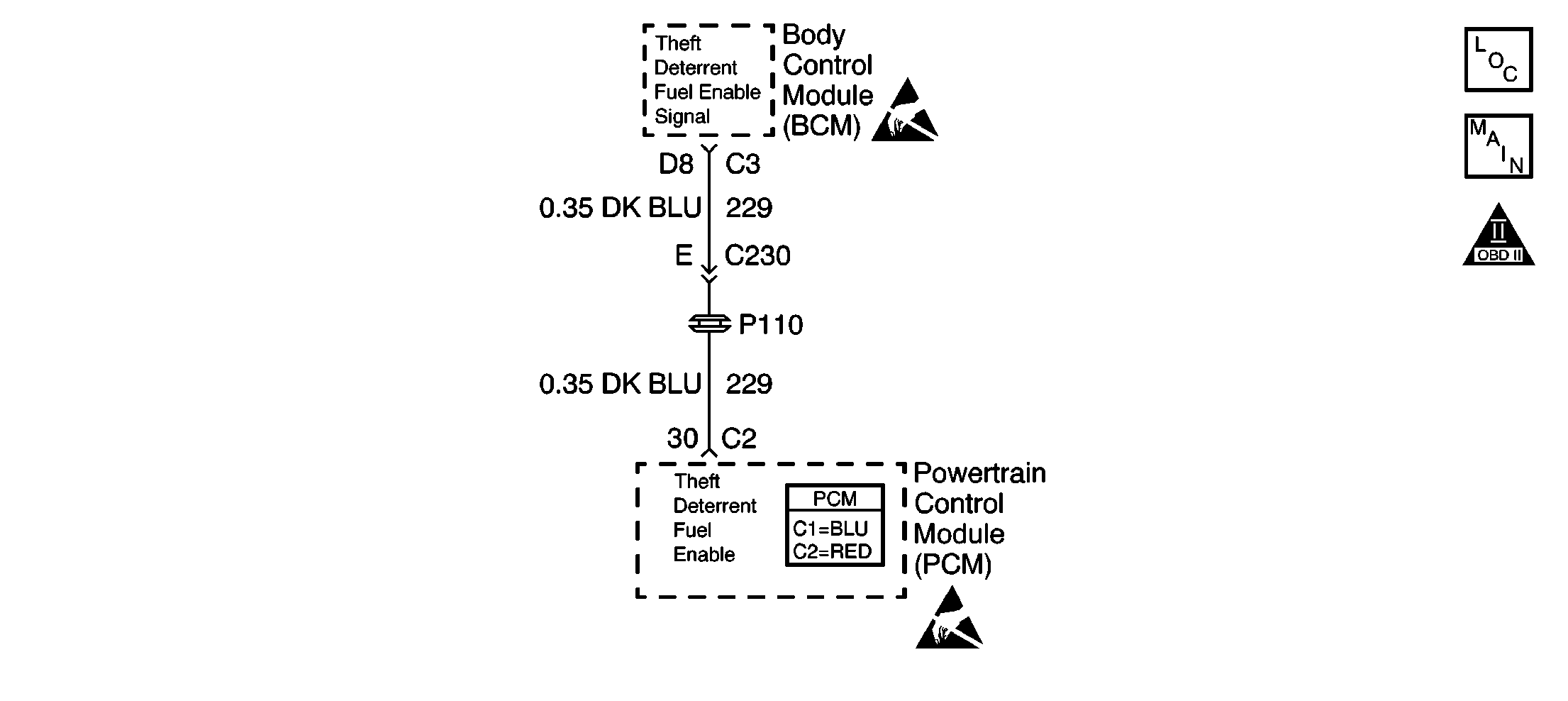
Circuit Description
The Vehicle Theft Deterrent system consists of the following components:
| • | Powertrain Control Module (PCM) |
| • | Body Control Module (BCM) |
| • | Ignition Lock and Key |
The Vehicle Theft Deterrent system is designed to disable vehicle operation if the incorrect key or starting procedure is used. The Body Control Module (BCM) enables the crank circuit to the starter and sends a signal to the PCM if the correct key is being used. If the proper signal does not reach the PCM on the fuel enable circuit, the PCM will not pulse the injectors ON and thus not allow the vehicle to continue to operate, even if the crank circuit is bypassed. The proper signal is between 40-60 Hz and is measured using the DMM set to the DC scale.
If a condition with the circuit occurs after the engine is started and running the PCM will not disable the fuel injectors. The PCM will continue to enable the fuel injectors because a correct signal from the BCM was received by the PCM on startup.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The Engine is in the run or start position.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The PCM does not receive the 40-60 Hz signal from the Body Control Module |
| • | Condition present for less than 1 second |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM stores the DTC information into memory when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illuminate. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. |
| • | The engine starts and then stalls or the starter does not engage. |
| • | If a condition with the circuit occurs after the engine is started and running the engine will start on the next ignition cycle. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important:
• Remove any debris from the PCM connector surfaces before servicing
the PCM. Inspect the PCM connector gaskets when diagnosing/replacing
the PCM. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets
prevent water intrusion into the PCM. • For any test that requires probing the PCM or component harness
connectors, use the J 35616
connector test adapter kit. Using this kit prevents damage to the
harness connector terminals. Refer to
Using Connector Test Adapters
in Wiring Systems.
Inspect the GAGE fuse for an open. An open GAGE fuse causes DTC P1626 to set and the starter does not operate. Refer to Testing for Short to Ground in Wiring Systems.
If the engine starts and then stalls, the Body Control Module is not suppling the appropriate signal or the theft deterrent fuel enable circuit is open, shorted to a ground, or shorted to a voltage.
For an intermittent condition, refer to Symptoms .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
An engine that does not crank and a DTC P1626 is set, indicates that there is a theft deterrent system condition. An incorrect ignition key or an incorrect starting procedure causes a no crank condition.
-
An engine that does not crank indicates there is a condition with the Body Control Module.
-
This step determines if the Powertrain Control Module is capable of sending a 5 volt signal to the BCM.
-
This step determines if the Body Control Module is capable of sending a signal to the PCM. The Body Control Module sends the PCM a 40-60 Hz signal.
-
This step determines if the condition is intermittent. If the engine starts and continues to operate, you may have corrected the condition during diagnoses. Inspect all connections at the BCM and the PCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
Does the engine crank? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Theft Deterrent in Theft Deterrent | ||||||||
Is the voltage near the specified voltage? | 5 volts | |||||||||
Is the hertz signal within the specified range? | 40-61 Hz | |||||||||
Does the engine start and continue to operate? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
7 | Test the theft deterrent fuel enable circuit for the following:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
8 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
9 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
10 |
Important:: Program the replacement PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
11 | Replace the Body Control Module. Refer to Body Control Module Replacement in Body Control Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
12 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||
13 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
