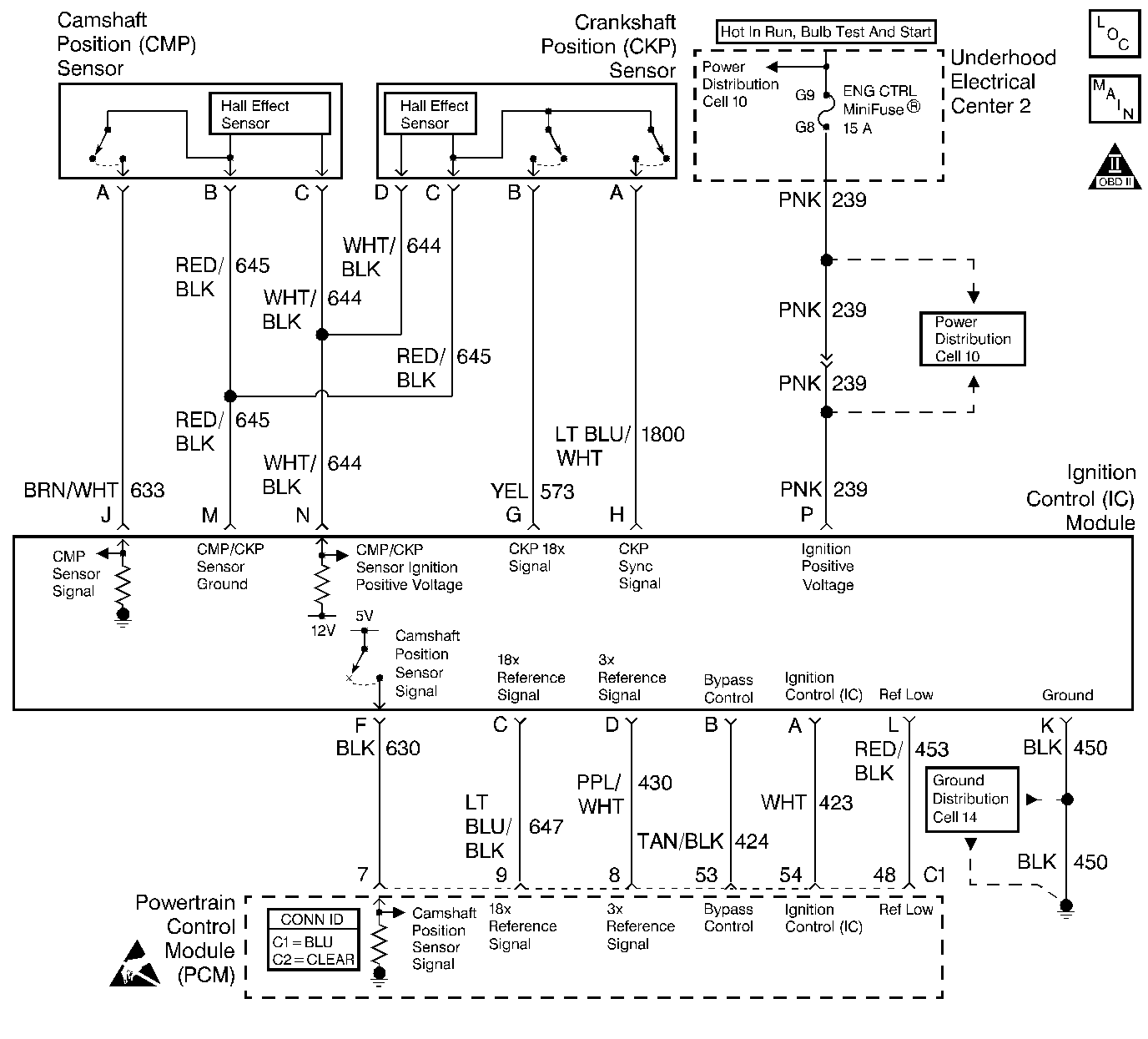
Circuit Description
The Electronic Ignition system uses a waste spark method of spark distribution. In this type of ignition system, the ignition control module triggers the correct coil based on the sync signal received from the crankshaft position sensor, resulting in both spark plugs connected to the coil firing at the same time. The spark plug for the cylinder on the exhaust stroke requires a lower energy requirement to fire, leaving the remaining high voltage to fire the spark plug for the cylinder on the compression stroke.
During crank, the ignition control module monitors the CKP sync signal. The CKP sync signal is used to determine the correct cylinder pair to fire first. The CKP sync signal is used only by the ignition control module to initiate ignition coil firing sequence. It is not passed to the PCM. After the ignition control module processes the CKP sync signal, the ignition control module monitors the 18X CKP signal and sends 18X and 3X reference pulses to the PCM. When the PCM receives these pulses, the PCM will command all six injectors to allow a priming shot of fuel for all the cylinders. After the priming, the injectors are left OFF during the next six 3X reference pulses from the ignition control module. This allows each cylinder a chance to use the fuel from the priming shot. During this waiting period, the PCM receives a camshaft position signal pulse. The camshaft position signal allows the PCM to operate the injectors sequentially based on camshaft position. If the camshaft position signal is not present at start-up, the PCM will begin sequential fuel delivery with a 1 in 6 chance that fuel delivery is correct.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insulation. Check for the following items:
| • | Poor connection or damaged harness. |
| Inspect the PCM harness and connectors for improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal to wire connection, and damaged harness. |
| • | Malfunctioning Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor. |
| Using a scan tool, compare Engine Coolant Temperature with Intake Air Temperature on a completely cool engine. Engine Coolant Temperature should be within 10°C of Intake Air Temperature. If not, replace the ECT sensor. |
| • | Throttle Position Sensor. |
| If the TP angle is over 80%, the PCM may operate in clear flood mode. The PCM will not allow fuel delivery while operating in clear flood mode. |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table:
-
Determines if the ignition control module (ICM) is receiving the 18X CKP Reference signal. If the 18X CKP signal to the ICM is not present, there will be no RPM, spark, or fuel injector pulses.
-
Ensures that the ICM has the proper voltage supply and ground.
-
Verifies that the ICM is supplying the proper sensor feed voltage.
-
Test for the proper operation of the CKP Sync signal, ICM and related spark system components. Without the CKP Sync signal the ICM is unable to properly sequence the ignition coils.
-
If the 18X and CKP Sync signals to the ICM or the 18X and 3X reference signals to the ICM short together the vehicle will not start and run. However, there will be spark and fuel injector pulses.
-
This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is replaced, the new PCM must be programmed.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
2 |
Important: Before proceeding with this table, ensure that the vehicle battery is fully charged. Important: If any DTCs are stored as failed since code clear, diagnose the DTCs before continuing with this table.
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
3 |
Does the fuel pressure measure within the specified values and holding? | 333-376 kPa (48-55 psi) | ||||||||||||||||||
4 | Is any fuel pressure indicated? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate an engine RPM? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
7 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? | B+ | |||||||||||||||||||
9 | Measure the voltage between the sensor signal and sensor ground circuits in the 18X sensor connector using a DMM. Does the voltage measure within the specified values? | 6V-9V | ||||||||||||||||||
10 | Inspect for poor connections at the 18X sensor. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
11 | Measure the voltage on the sensor feed circuit at the 18X sensor connector using a DMM that is connected to a good ground. Does the voltage measure near the specified value? | B+ | ||||||||||||||||||
12 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
13 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
14 |
Does the DMM indicate any voltage? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
15 | Locate and repair the short to voltage on the 18X sensor signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
16 |
Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
17 |
Did the injector test lamp illuminate for any of the injectors? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
18 |
Did the injector test lamp illuminated for any of the injectors? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
19 |
Did the injector test lamp blink for each injector? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
20 | Did the injector test lamp blink for any of the injectors? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
21 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
22 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
23 | Locate and repair the open ignition positive feed circuit to the fuel injectors. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
Did you observe spark at all cylinders? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
25 | Did you observe spark at any cylinder? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
26 |
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? | 6V-9V | ||||||||||||||||||
27 | Inspect for poor connections at the 18X sensor. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis and Connector Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
28 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
29 |
Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
30 |
If a problem is found, replace the damaged ignition component(s). Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
31 | Measure the ignition coil secondary resistance using a DMM. If any resistance is outside the specified values, replace the malfunctioning ignition coil(s) as necessary. Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement . Did you find and correct the condition? | 5K-8K ohms (5000 - 8000 ohms) | ||||||||||||||||||
32 | Measure the resistance of the ignition wires associated with the cylinders that did not have spark using a DMM. Replace the ignition wire(s) that measure more than the specified value. Refer to Spark Plug Wire Harness Replacement . Did you find and correct the condition? | 3280-4921 ohms/meter(1000-1500 ohms/ft) | ||||||||||||||||||
33 |
Does the test lamp blink continuously while the engine is cranking? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
34 |
Did the spark plug inspection reveal excessive fouling? | -- | Go to Base Engine Misfire Diagnosis in Engine Mechanical | |||||||||||||||||
Test for the following condition(s):
If a problem is found, repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
36 | Test the fuel for contamination. Refer to Alcohol/Contaminants-in-Fuel Diagnosis . If a problem is found, clean the fuel system and correct the contaminated fuel conditions as necessary. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
37 | Repair the engine mechanical problem. Refer to Base Engine Misfire Diagnosis in Engine Mechanical to diagnose the following condition(s):
Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
38 | Inspect for poor connections at the ICM. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis and Connector Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
39 | Locate and repair the open in the ICM ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
40 | Locate and repair the open in the ignition positive feed circuit to the ICM. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
41 | Replace the 18X CKP sensor. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
42 | Replace the ICM. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
43 | Locate and repair the short to ground in the fuel injector control circuit(s) associated with the injector test lamp(s) that stayed illuminated. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
44 | Inspect for poor connections at the PCM. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis and Connector Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
45 | Replace the ignition coil(s) associated with the cylinder(s) that did not have spark. Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
|
Important: Replacement PCM must be reprogrammed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- |
