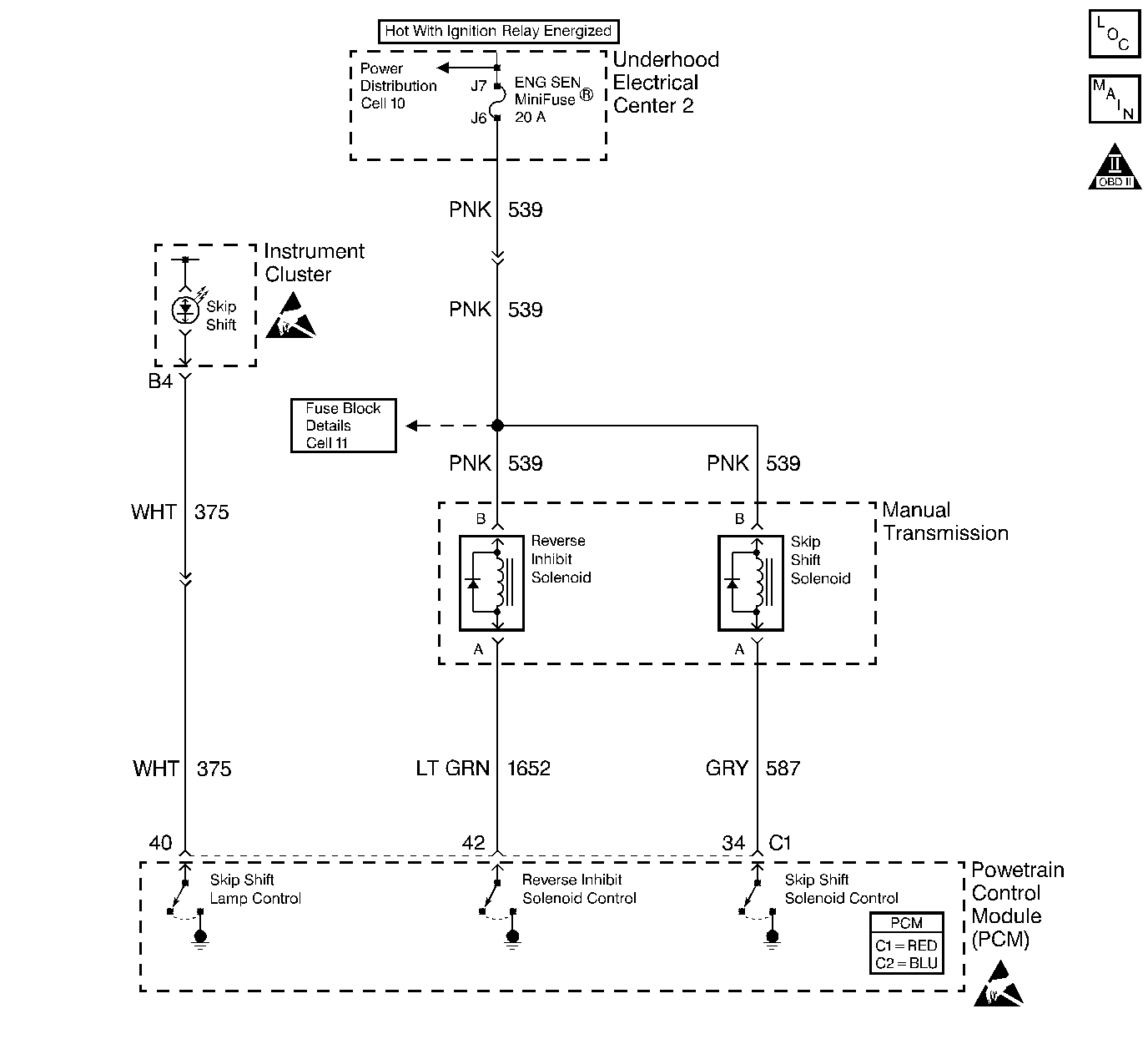
Circuit Description
An ignition voltage is supplied to the Skip Shift Lamp. The PCM controls the lamp by grounding the control circuit via an internal switch called a driver. The driver supplies the ground for the component being controlled. Each driver has a fault line which the PCM monitors. When the PCM commands a component ON, the voltage of the control circuit should be low (near 0 volts). When the PCM commands the control circuit to a component OFF, the voltage potential of the circuit should be high (near battery voltage). If the fault detection circuit senses a voltage other than what is expected, the fault line status changes causing the DTC to set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine speed is greater than 600 RPM. |
| • | Ignition voltage greater than 6.0 volts but less than 16 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The PCM detects that the commanded state of the driver and the actual state of the control circuit do not match. |
| • | All conditions exist for a minimum of 10 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The powertrain control module (PCM) stores the DTC information into memory when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will not illuminate. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Using the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data determines how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also aid determining how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that you observed. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
If the I/P is completely inoperative, refer to Instrument Cluster System Check in Instrument Panel, Gauges and Console for further diagnosis.
For an intermittent, refer to Symptoms .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Listen for an audible click when the solenoid operates. Command both the ON and the OFF states. Repeat the commands as necessary.
-
If you do not find any trouble in the control circuit or the connection at the PCM, the PCM may be faulty. However, this is an extremely unlikely failure.
-
The repair is not complete if the scan tool indicates that the diagnostic ran and failed.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||
|
Important: If the I/P is completely inoperative, refer to Instrument Cluster System Check in Instrument Panel, Gauges and Console for further diagnosis.
Does the shift lamp turn ON and OFF when commanded? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
3 |
Is the shift lamp OFF? | -- | ||||||||
4 | Probe the shift lamp control circuit in the PCM harness connector with a fused jumper wire connected to ground. Refer to Probing Electrical Connectors in Wiring Systems. Is the shift lamp ON? | -- | ||||||||
5 | Repair the short to ground in the shift lamp control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
6 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
7 | Test for the following conditions:
Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
|
Important:: Program the replacement PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate that this test passed? | -- | |||||||||
10 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
