Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
Heated O2 Sensors
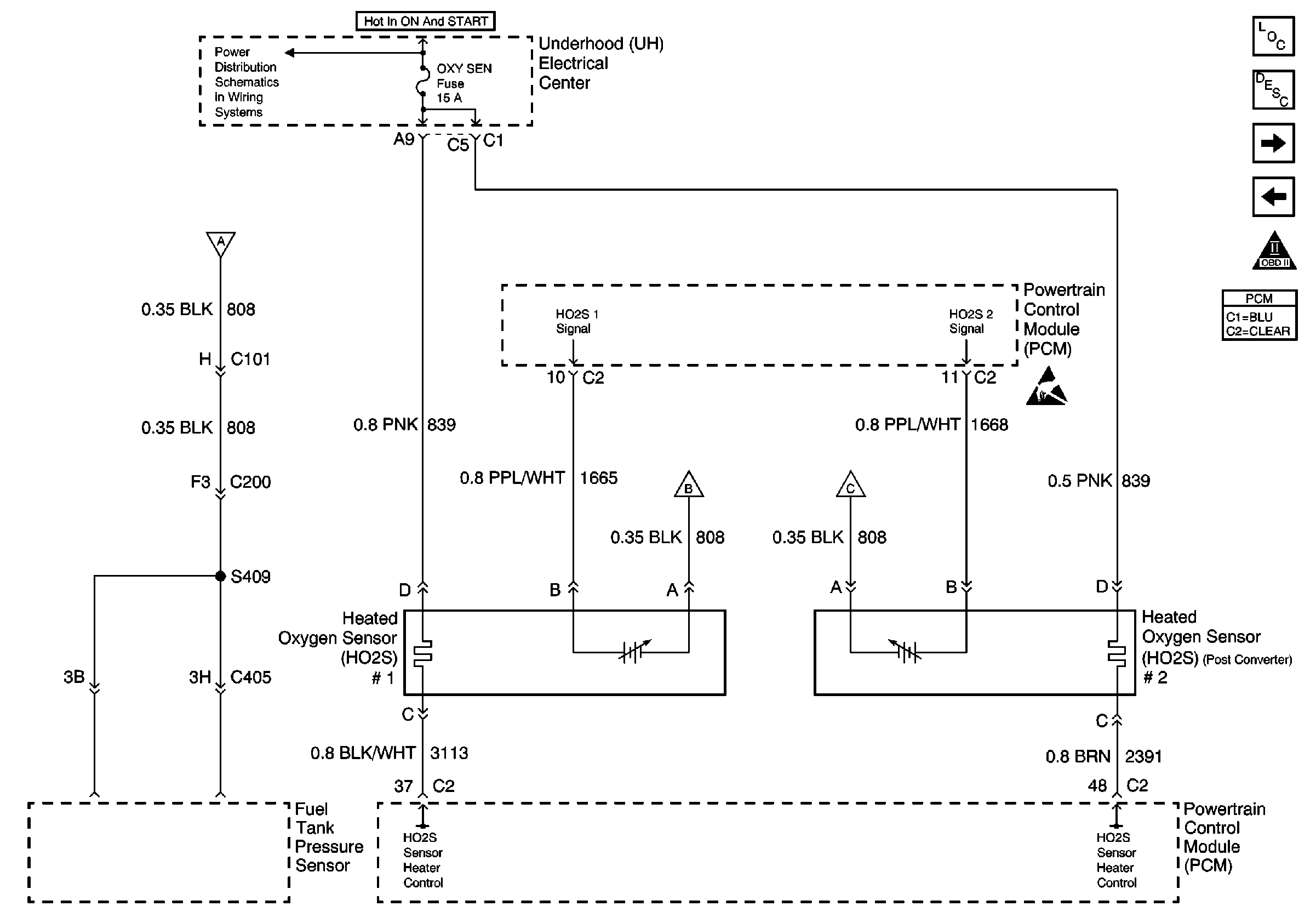
.
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) continuously monitors the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) activity for 100 seconds. During the monitor period the PCM counts the number of times that the HO2S transitions from rich to lean and from lean to rich and adds the amount of time it took to complete all transitions. With this information, an average time for all transitions can be determined. The PCM then divides the rich to lean average by the lean to rich average to obtain a ratio. If the HO2S transition time ratio is not within range, DTC P1134 will set, indicating that the oxygen sensor is not responding as expected to changes in exhaust oxygen content.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The following types of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are not active: |
| • | Fuel trim |
| • | Fuel injector circuit |
| • | Misfire |
| • | Evaporative emission (EVAP) system |
| • | Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system |
| • | AIR system |
| • | Throttle position (TP) sensor |
| • | Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor |
| • | Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor |
| • | Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor |
| • | Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor |
| • | Mass air flow (MAF) sensor |
| • | DTCS P0131, P0132, or P0135 are not set |
| • | The ystem voltage is more than 9 volts. |
| • | The engine is running in closed loop |
| • | The engine is running for at least 3.3 minutes. |
| • | The ECT is more than 75°C (167°F) |
| • | The engine speed is between 1,000-3,000 RPM |
| • | The MAF is between 15-40 gm/s |
| • | The above conditions are stable for 3 seconds |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects degraded, or slow, rich to lean or lean to rich response times for HO2S 1.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive drive trips during which the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A last test failed, or the current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no other emission related diagnostic failures are reported. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL diagnostic trouble code. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
A malfunction in the HO2S heater ignition feed or ground circuit may cause the DTC to set. Check HO2S heater circuitry for intermittent malfunctions or poor connections. If connections and wiring are OK and the DTC continues to set, the HO2S may be at fault..
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition occurs that caused the DTC to set. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
HO2S contamination may cause multiple HO2S diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to set.
-
The use of leaded fuel may be indicated by the removal or tampering of the fuel filler restrictor.
An HO2S contaminated by silicon will have a white, powdery deposit on the portion of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream. The usual cause of silica contamination is the use of unapproved silicon RTV engine gasket material, the use of silicon based sprays or fluids within the engine or coolant consumption. Phosphorus contamination also leaves a white powdery coating on the HO2S. Phosphorus contamination comes from oil consumption. If the cause of this contamination is not corrected, the replacement HO2S will also get contaminated.
-
Even small exhaust leaks can cause slow response from the HO2S.
-
An HO2S contaminated by silicon will have a white, powdery deposit on the portion of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream. The usual cause of silica contamination is the use of un-approved silicon RTV engine gasket material, the use of silicon based sprays or fluids within the engine or coolant consumption. Phosphorus contamination also leaves a white powdery coating on the HO2S. Phosphorus contamination comes from oil consumption. If the cause of this contamination is not corrected, the replacement HO2S will also get contaminated.
-
If the voltage observed in step 8 is less than the range specified, a short between the high and low circuits or a short between the high circuit and ground is indicated. With the HO2S and the PCM disconnected, the resistance between the high and low circuits and the resistance between the high circuit and ground should measure infinite.
If the voltage observed in step 8 is more than the range specified, a short between the high circuit and an ignition voltage source is indicated.
-
If the voltage observed in step 9 is not below the voltage specified, a high resistance (open) high or low circuit is indicated.
Good circuit continuity measures less than 5 ohms with the PCM and sensor disconnected. Measure between the PCM connector and the HO2S connector. Ensure PCM terminal contact is good.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Is DTC P0140 also set? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3 | Are any powertrain component DTCs set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTCs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Has the contamination source been removed and the affected sensors replaced? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5 |
Did this DTC run and fail this ignition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6 | The condition that set this DTC is not present. This DTC may have been set by one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above or similar engine conditions as necessary. Was a condition found and repaired? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Was a repair made? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
Is the HO2S voltage within the value range specified? | 351-551 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
9 |
Is the HO2S voltage less than the value specified? | 20 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
11 | Connect the test lamp between the engine harness side of the HO2S heater ignition feed circuit terminal and the engine harness side of the HO2S heater ground circuit terminal. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
HO2S contamination sources include the following:
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
15 | Repair the HO2S heater ignition feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
16 | Repair the HO2S heater ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
17 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
18 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
19 | Review the Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
