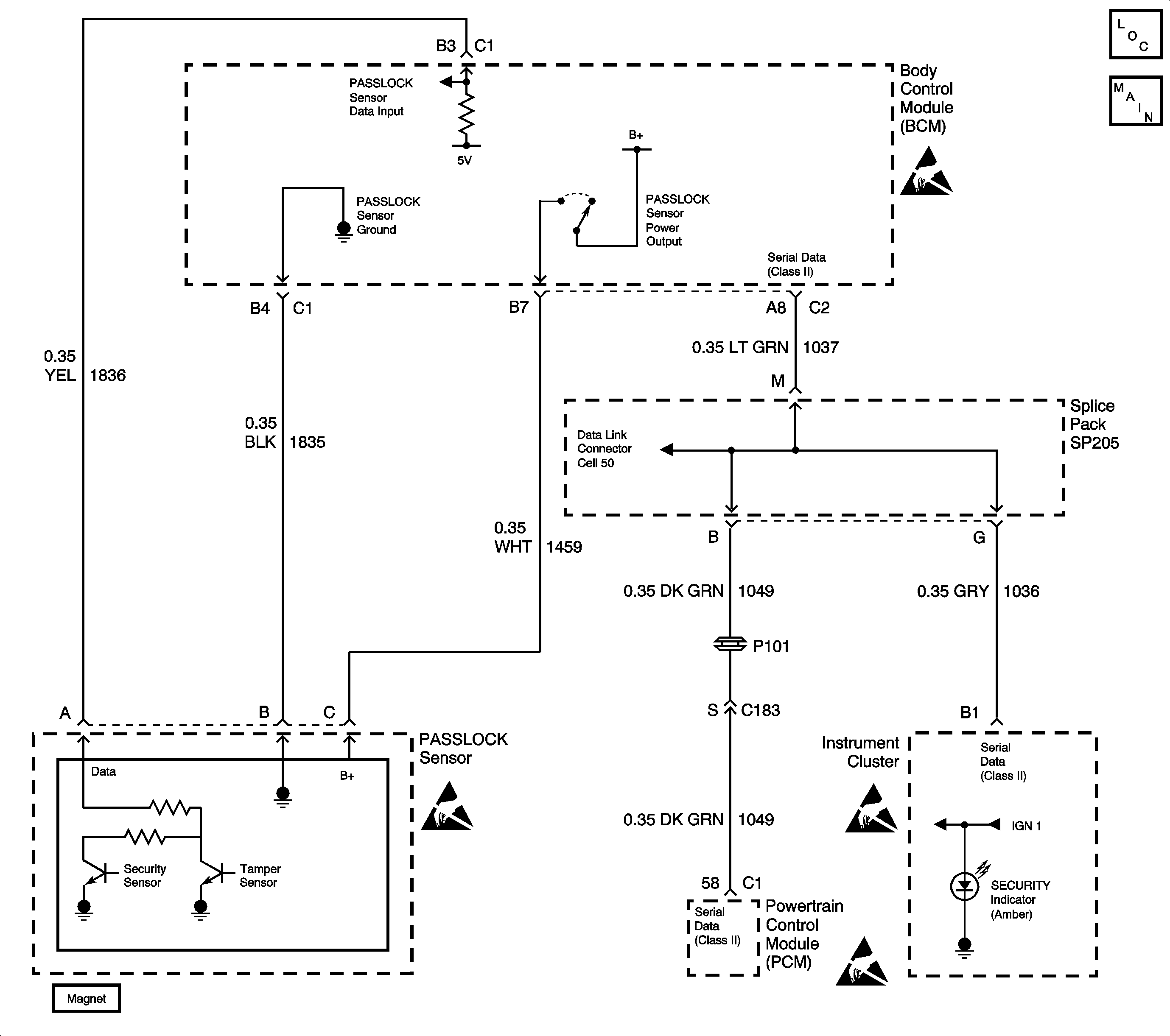
Circuit Description
The Passlock theft deterrent system contains a Passlock sensor. The Passlock sensor is part of the ignition lock cylinder assembly. The Body Control Module (BCM) provides voltage (B+) to the Passlock sensor through circuit 1459 when the ignition switch is in the accessory, on, or start. The BCM also provides ground to the Passlock sensor through circuit 1835. The Passlock sensor interfaces with the BCM through the Passlock detection circuit 1836.
When turning the ignition switch to the start position with the proper key, the Passlock sensor generates an analog voltage signal. This signal is sent through the Passlock detecting circuit. This analog voltage signal is of a specific value to the vehicle, and varies from vehicle to vehicle. When attempting to start the engine, the BCM compares a preset stored analog voltage value with the signal coming from the sensor. Because both values match, the BCM sends a fuel enable password via the Class II serial data link to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). As a result, the PCM enables the crank relay, and allows fuel delivery to the engine.
When attempting to start the engine by means other than using the proper key in the ignition switch, the Passlock sensor sends an analog voltage signal of a different value. The BCM compares the preset stored analog voltage value with the signal coming from the sensor. Because both values do not match, the BCM sends a fuel disable password via the Class II serial data link to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). As a result, the PCM disables the crank relay, and stops fuel delivery to the engine.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The analog voltage signal sampled at the BCM's Passlock detection circuit is one of 9 valid but incorrect Passlock sensor analog voltage signal ranges; signaling an invalid Passlock detection. |
| • | Condition must be present during an engine start attempt, or for one second anytime after the engine has started. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The BCM will take one of two actions:
- If the Passlock sensor analog voltage signal sample is out of range when attempting to start the vehicle, then the BCM:
- If the Passlock sensor analog voltage signal sample is initially the proper value (and the engine starts), but later on (during the same ignition cycle) the Passlock sensor analog voltage signal is out of range, then the BCM:
| • | Stores DTC B2960 in memory. |
| • | Sends a message to the instrument cluster to flash the SECURITY indicator. |
| • | The BCM sends a message to the PCM via Class II serial data link to disable the crank relay, and stops fuel delivery to the engine. |
| • | Disables the sampling of the Passlock sensor analog voltage signal for a time-out period of ten minutes. |
| • | If the ignition switch is left on for at least ten minutes, the BCM enters the theft deterrent re-learn mode. Refer to Body Control Module (BCM) Programming/RPO Configuration for more information, OR |
| • | Stores DTC B2960 in the BCM memory. |
| • | The BCM enters fail-enable mode. |
| • | Sends a message to the instrument cluster to turn on the SECURITY indicator. |
| • | Upon subsequent engine start attempts, the BCM will send a message to the PCM via Class II serial data link to enable the crank relay, and to deliver fuel to the engine. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A current DTC B2960 clears when the BCM detects the correct Passlock sensor analog voltage signal on the Passlock detection circuit 1836. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 100 consecutive ignition cycles if the condition for the malfunction is no longer present. |
| • | Using a scan tool. Refer to Clearing DTCs for more information. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | The following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction to occur: |
| - | Excessive resistance in the Passlock detection circuit 1836. |
| - | Poor connections at the BCM or the Passlock sensor electrical connector. |
| • | If the Passlock sensor analog voltage signal is incorrect, then there will be no communication from the BCM to the PCM to enable the crank relay and to enable fuel delivery to the engine. This vehicle disable period state will last approximately ten minutes during which time the SECURITY indicator will flash when the ignition switch is on. Disconnecting the battery will not clear the timer sequence, it will resume when battery power is restored. Even if a proper Passlock sensor analog voltage signal is read during the vehicle disable period, the vehicle will not start until the ten minute time period has elapsed. After this ten minute time period, the SECURITY indicator will change from a flashing state to a solid on state. At this time, the BCM enters the theft deterrent re-learn mode. Also, the engine will start if the BCM detects the correct Passlock sensor analog voltage signal. |
| • | Check for poor connections at both the BCM and the ignition lock cylinder assembly, these could cause an open, incorrect Passlock sensor voltage signal, or intermittent malfunction. If the DTC is a history DTC, the problem may be intermittent. Try performing the tests shown while moving wiring, connectors, and the key, this can often cause the malfunction to appear. |
| • | DTC B2958 may set in the BCM when the ignition switch is on with the Passlock sensor electrical connector disconnected. When BCM diagnostics and repairs are completed for DTC B2960, clear BCM DTCs and perform the BCM Diagnostic System Check. Refer to Diagnostic System Check - Body Control System |
| for more information. |
| • | DTC P1626 will set in the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) when the ignition switch is on with the Body Control Module (BCM) disconnected. When BCM diagnostics and repairs are completed, refer to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check (LX5) or Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check (L36) in Engine Controls for additional information on PCM related DTCs. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
Always perform the BCM diagnostic system check before attempting to diagnose this DTC.
-
This DTC may set when the Theft Deterrent Re-Learn procedure was not performed after a ignition lock cylinder assembly replacement.
-
DTC B2723 identifies an open or short to B+ in circuit 1836.
-
Checks for power to the PASSLOCK sensor.
-
Checks for a faulty BCM not grounding the PASSLOCK sensor.
-
Checks for an open in circuit 1835.
-
Checks for an open in circuit 1459.
-
Determines whether the BCM is not reading properly the voltage signal from the PASSLOCK sensor.
-
Determines whether the PASSLOCK sensor is faulty and not due to excessive voltage level sample in circuit 1836.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the BCM diagnostic system check performed? | -- | |||
Was the ignition lock cylinder replaced? | -- | |||
Is DTC B2958 also set as a current DTC in the BCM? Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Displaying for more information. | -- | |||
Is the voltage measured within the specified range? | B+ (10-14V) | |||
Using a DMM, measure the resistance by backprobing between the BCM harness connector C1 terminal D3 and BCM harness connector C3 terminal D. Is the resistance measured within the specified range? | Less than 2ohms | |||
Is the resistance measured within the specified range? | Less than 2ohms | |||
Is the voltage measured within the specified range? | B+ (10-14V) | |||
Is the PASSLOCK voltage output displayed on the scan tool same (+/- 0.5V) as the voltage measured with the DMM? | -- | |||
Is the resistance measured within the specified range? | Less than 2ohms | |||
10 |
Does this DTC reset as a current DTC? | -- | System OK | |
11 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
12 | Repair poor connection or open in circuit 1835. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Repair poor connection or open in circuit 1459. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
14 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | ||
15 | Repair poor connection or open in circuit 1836. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
16 |
Are there any current BCM DTCs present? | -- | System OK |
