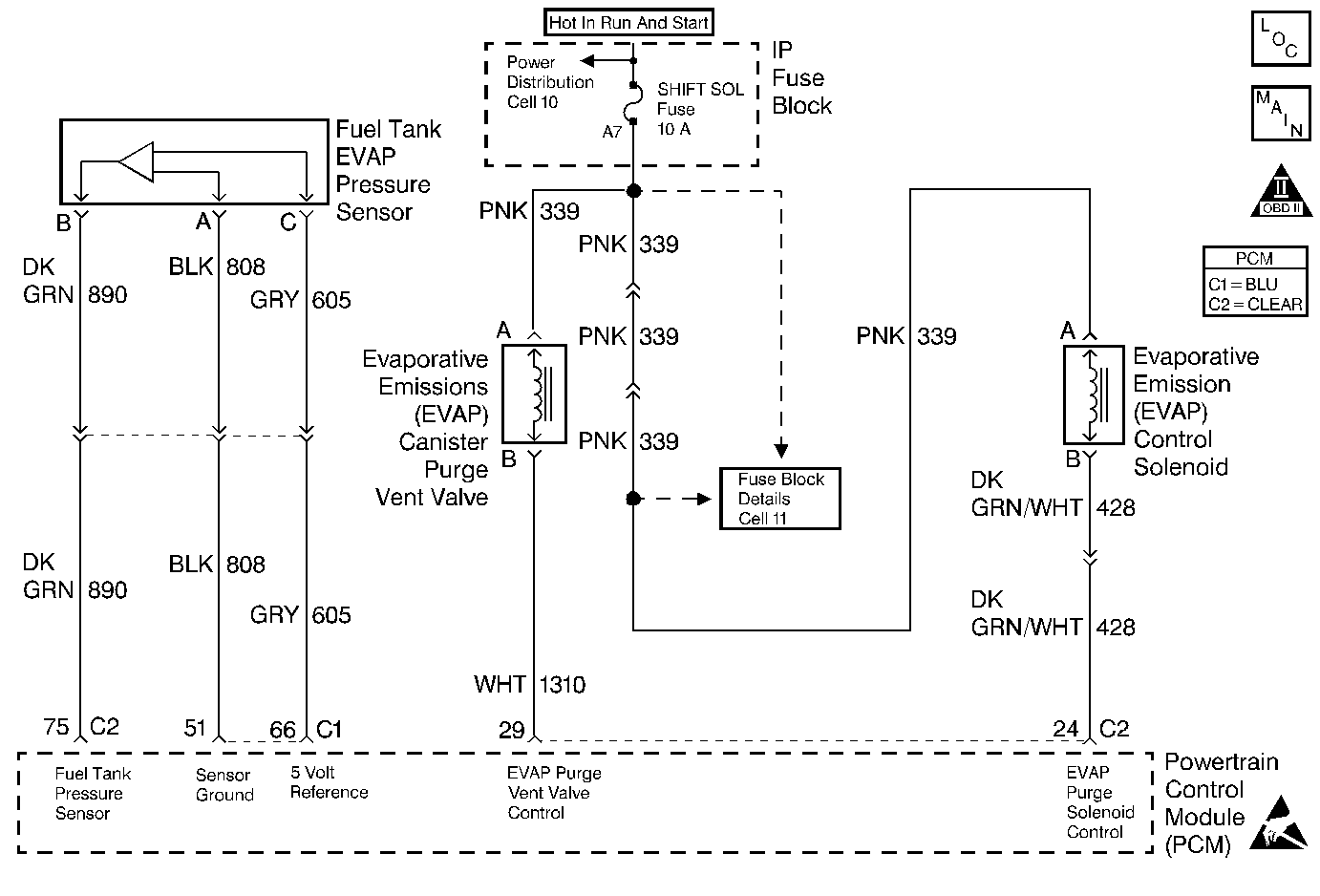
Circuit Description
The PCM tests the EVAP system for the following conditions:
| • | Large and small leaks (P0440 and P0442) |
| • | Excess vacuum (P0446) |
| • | Purge flow during non-commanded conditions (P1441) |
| • | Fuel Pressure sensor and Fuel Level sensor faults (P0452, P0453, P0461, P0462 and P0463) |
| • | EVAP Purge and Vent Valve faults (P1645 and P1646) |
The PCM monitors the amount of vacuum in the EVAP system by monitoring the Fuel Tank Pressure sensor. For this DTC the PCM turns ON both the EVAP Purge Valve and the EVAP Vent Valve when the Conditions for Running the DTC are met. This applies an engine vacuum to a closed EVAP system. The PCM turns OFF the EVAP Purge Valve when the system reaches the correct amount of vacuum. With the EVAP Purge Valve OFF and with the EVAP Vent Valve ON, the EVAP system should HOLD the vacuum in the EVAP system. This test will indicate a small leak if the EVAP system fails to hold enough vacuum for a specific length of time. This DTC will set after two consecutive failures of the above test.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTC's P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0135, P0141, P0151, P0152, P0153, P0154, P0452, P0453, P0503, P1111, P1112, P1114, P1115, P1133 or P1153 are not set. |
| • | Battery voltage is between 10.5 and 17.5 volts. |
| • | Barometric pressure is more than 71.78 kPa. |
| • | Fuel level is between 10% and 89.8% of full capacity for at least 3.2 seconds continuously. The time limit is required because fuel sloshing within the tank may cause the fuel level indication to vary outside the fuel level limits. |
| • | Coolant temperature is between 2°C and 32.7°C. |
| • | Intake air temperature is between 2°C and 32.7°C |
| • | Start up coolant and intake air temperature are within 14.2°C of each other. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The vacuum in the EVAP system decays (leaks) too fast.
Important: This DTC does NOT report a first failed test. A first fail of this DTC will have a scan tool status as Not Run. Use the scan tool data display parameter of EVAP TEST RESULT to determine if this DTC has failed or passed for THIS ignition cycle.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) after two consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the DTC sets. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
| • | A first failure of this DTC will NOT store as Last Test Failed or History. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A Last Test Failed DTC will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive warm-up cycles with no failures of any diagnostic test. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear DTCs. |
| • | Interrupting PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes in Powertrain Control Module Description . |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: An accurate indication of fuel level is required for the PCM to properly Pass or Fail this DTC. Always diagnose fuel level sensor DTC's before performing this DTC's diagnostic table. Always check for fuel level sensor DTC's stored as History.
Perform a physical inspection of the EVAP system. Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | A loose, missing, defective, or incorrect fuel tank cap |
| • | Incorrectly routed or defective EVAP system vacuum and vapor lines |
| • | A malfunctioning or damaged vapor canister |
Inspect for charcoal release from the vapor canister. Refer to Evaporative Emission System Cleaning
The vacuum and pressure in the EVAP system is measured in inches of H2O (water). Most gauges measure vacuum in inches of Hg (mercury) and pressure in psi (pounds per square inch). The following shows how the values compare:
in. H2O | in. Hg. | psi |
|---|---|---|
1 in. H2O | 0.07 in. Hg | 0.0361 psi. |
5 in. H2O | 0.36 in. Hg | 0.180 psi. |
10 in. H2O | 0.73 in. Hg | 0.361 psi. |
15 in. H2O | 1.10 in. Hg | 0.541 psi. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
Inspect the service port. Make sure that the dust cap and valve core is not loose or damaged (the valve core may have left hand threads). If service port leakage is suspected use the following procedure:
Disconnect the purge line from the EVAP Purge solenoid valve.
Connect a hand vacuum pump to the service port by placing the hose/adaptor over the unthreaded end portion of the service port.
Apply vacuum to 5 in. Hg. If the vacuum does not hold replace the service port (may require line replacement).
-
If the vehicle passes the Service Bay Test then an intermittent leak had occurred. Check the fuel tank cap for a possible loose or leaking condition that may have caused this DTC to set.
If the Service Bay Test can not be run, proceed to Step 5. If a fault is not currently present the diagnostic table steps will return you to Step 3.
-
Refer to the information supplied with the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic cart on proper setup and adjustment procedures.
-
If a leak was not found in Step 9 and the vehicle is equipped with On Board Refueling Vapor Recovery (Aurora or Seville) connect the EVAP pressure/purge Diagnostic station with the fuel cap adaptor to the fuel tank filler neck and repeat Step 9. These (ORVR) vehicles are equipped with a check valve at the base of the filler tube which will not allow pressure from the EVAP service port to be applied to the filler tube and the fuel cap.
An EVAP Pressure sensor that does not correctly respond to pressure or vacuum will cause this DTC to set.
The EVAP Pressure Sensor monitors a range from 7.5 in. H2O of pressure to -17.5 in. H2O of pressure (vacuum).
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||
2 | Check for DTC's P0440, P0446, P0452, P0453, P0461, P0462, P0463, P1441, P1645 and P1646. Are any other EVAP system DTC's stored in HISTORY? | -- | Go to DTC's that are set. | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||
Inspect the EVAP system for the following conditions:
Repair the EVAP system if needed. Was a repair made to the EVAP system? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Go to Step 4 | |||||||||
|
Important: Before proceeding with the Service Bay Test the vehicle must meet the
following operating criteria:
If any of the above conditions are not met the scan tool will display Test Aborted upon activating the Service Bay Test.
Does the vehicle pass the Service Bay Test? | -- | Fault not present. Refer to Test Descriptions | Go to Step 5 | |||||||||
5 |
Can the specified value of vacuum be obtained and held? | 12 in. Hg. | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||
6 |
Can the specified value of vacuum be obtained and held? | 5 in. Hg. | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||||
7 |
Can the specified value of vacuum be obtained and held? | 5 in. Hg. | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||||
8 |
Was the EVAP Vent line replaced? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Go to Step 12 | ||||||||
|
Important: The following steps require the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic station J 41413 and the ultrasonic leak detector J 41416. Always zero the EVAP Pressure and Vacuum (in. H2O) gauges on the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic station before proceeding with diagnosis.
Important: Do Not apply more than 15 in. H2O of pressure to the EVAP system. Was a leak found and repaired? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Go to Step 13 | |||||||||
10 |
Important: Inspect the EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve and the purge line for carbon contamination. Refer to Diagnostic Aids . Replace the EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- | ||||||||
11 | Replace the EVAP Vent Valve. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- | ||||||||
12 | Replace the EVAP Vapor Canister. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- | ||||||||
Do both values indicate the same amount of vacuum in the EVAP system to within the range specified? | + or - 2 in. H2O | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 14 | |||||||||
14 | Replace the EVAP Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
