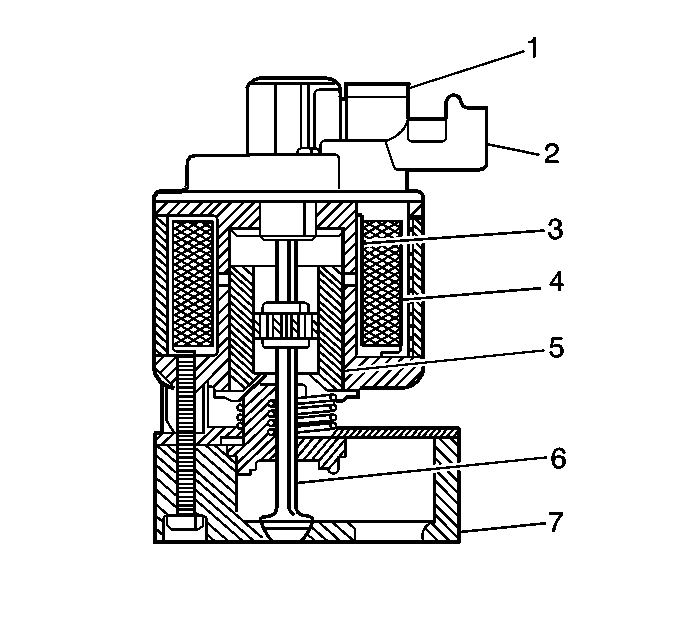
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is used to reduce the amount of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission levels caused by combustion temperatures exceeding 816°C (1,500°F). It does this by introducing small amounts of exhaust gas back into the
combustion chamber. The exhaust gas absorbs a portion of the thermal energy produced by the combustion process and thus decreases combustion temperature. The EGR system will only operate under specific temperature, barometric pressure and engine load conditions
in order to prevent driveability concerns and to increase engine performance.